Obfuscapk is a modular Python tool for obfuscating Android apps without needing their source code, since apktool is used to decompile the original apk file and to build a new application, after applying some obfuscation techniques on the decompiled smali code, resources and manifest. The obfuscated app retains the same functionality as the original one, but the differences under the hood sometimes make the new application very different from the original (e.g., to signature based antivirus software).
❱ Demo
❱ Architecture
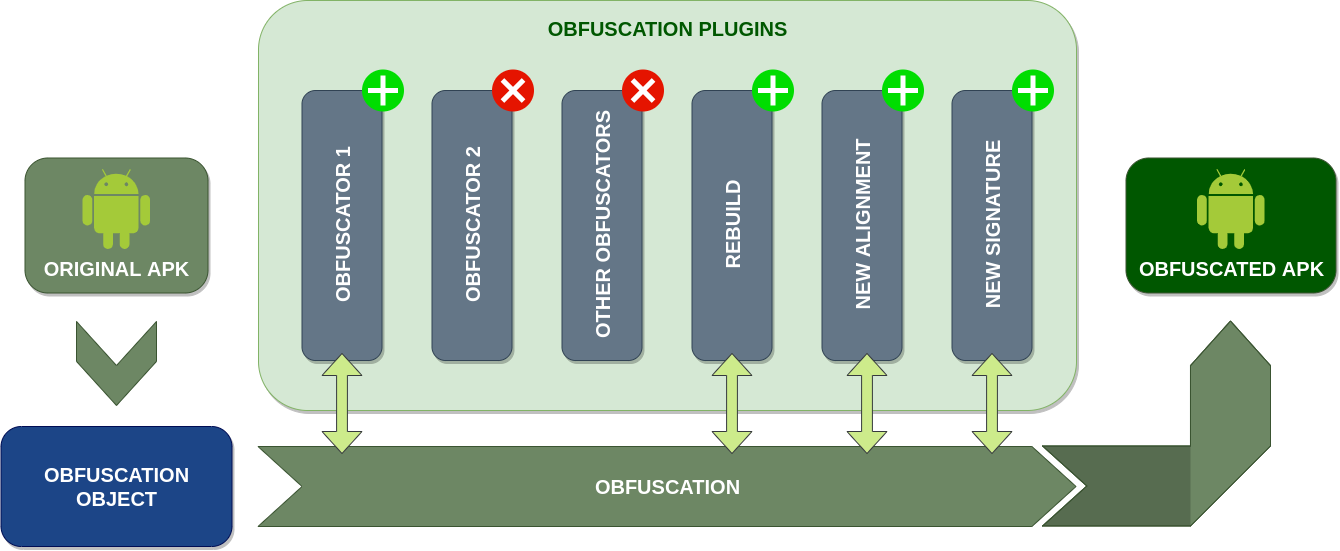
Obfuscapk is designed to be modular and easy to extend, so it’s built using a plugin system. Consequently, every obfuscator is a plugin that inherits from an abstract base class and needs to implement the method obfuscate . When the tool starts processing a new Android application file, it creates an obfuscation object to store all the needed information (e.g., the location of the decompiled smali code) and the internal state of the operations (e.g., the list of already used obfuscators). Then the obfuscation object is passed, as a parameter to the obfuscate method, to all the active plugins/obfuscators (in sequence) to be processed and modified. The list and the order of the active plugins is specified through command line options.
The tool is easily extensible with new obfuscators: it’s enough to add the source code implementing the obfuscation technique and the plugin metadata (a <obfuscator-name>.obfuscator file) in the src/obfuscapk/obfuscators directory (take a simple existing obfuscator like Nop as a starting example). The tool will detect automatically the new plugin, so no further configuration is needed (the new plugin will be treated like all the other plugins bundled with the tool).
❱ Obfuscators
The obfuscators included in Obfuscapk can be divided into different categories, depending on the operations they perform:
- Trivial : as the name suggests, this category includes simple operations (that do not modify much the original application), like signing the apk file with a new signature.
- Rename : operations that change the names of the used identifiers (classes, fields, methods).
- Encryption : packaging encrypted code/resources and decrypting them during the app execution. When Obfuscapk starts, it automatically generates a random secret key (32 characters long, using ASCII letters and digits) that will be used for encryption.
- Code : all the operations that involve the modification of the decompiled source code.
- Resources : operations on the resource files (like modifying the manifest).
- Other
The obfuscators currently bundled with Obfuscapk are briefly presented below (in alphabetical order). Please refer to the code for more details.
NOTE: not all the obfuscators below correspond to real obfuscation techniques (e.g., Rebuild , NewSignature , NewAlignment and VirusTotal ), but they are implemented as obfuscators in order to keep the architecture modular and easy to extend with new functionality.
AdvancedReflection [Code]
Uses reflection to invoke dangerous APIs of the Android Framework. In order to find out if a method belongs to the Android Framework, Obfuscapk refers to the mapping discovered by Backes et al.
ArithmeticBranch [Code]
Insert junk code. In this case, the junk code is composed by arithmetic computations and a branch instruction depending on the result of these computations, crafted in such a way that the branch is never taken.
AssetEncryption [Encryption]
Encrypt asset files.
CallIndirection [Code]
This technique modifies the control-flow graph without impacting the code semantics: it adds new methods that invoke the original ones. For example, an invocation to the method m1 will be substituted by a new wrapper method m2 , that, when invoked, it calls the original method m1 .
ClassRename [Rename]
Change the package name and rename classes (even in the manifest file).
ConstStringEncryption [Encryption]
Encrypt constant strings in code.
DebugRemoval [Code]
Remove debug information.
FieldRename [Rename]
Rename fields.
Goto [Code]
Given a method, it inserts a
gotoinstruction pointing to the end of the method and anothergotopointing to the instruction after the firstgoto; it modifies the control-flow graph by adding two new nodes.
LibEncryption [Encryption]
Encrypt native libs.
MethodOverload [Code]
It exploits the overloading feature of the Java programming language to assign the same name to different methods but using different arguments. Given an already existing method, this technique creates a new void method with the same name and arguments, but it also adds new random arguments. Then, the body of the new method is filled with random arithmetic instructions.
MethodRename [Rename]
Rename methods.
NewAlignment [Trivial]
Realign the application.
NewSignature [Trivial]
Re-sign the application with a new custom signature.
Nop [Code]
Insert junk code. Nop, short for no-operation , is a dedicated instruction that does nothing. This technique just inserts random
nopinstructions within every method implementation.
RandomManifest [Resource]
Randomly reorder entries in the manifest file.
Rebuild [Trivial]
Rebuild the application.
Reflection [Code]
This technique analyzes the existing code looking for method invocations of the app, ignoring the calls to the Android framework (see
AdvancedReflection). If it finds an instruction with a suitable method invocation (i.e., no constructor methods, public visibility, enough free registers, etc.) such invocation is redirected to a custom method that will invoke the original method using the Reflection APIs.
Reorder [Code]
This technique consists of changing the order of basic blocks in the code. When a branch instruction is found, the condition is inverted (e.g., branch if lower than , becomes branch if greater or equal than ) and the target basic blocks are reordered accordingly. Furthermore, it also randomly re-arranges the code abusing
gotoinstructions.
ResStringEncryption [Encryption]
Encrypt strings in resources (only those called inside code).
VirusTotal [Other]
Send the original and the obfuscated application to Virus Total. You must provide the VT API key (see
-koption).
 !
!